Engine Functionality
A diagram for Proof Frog’s engine functionality in full is presented below.
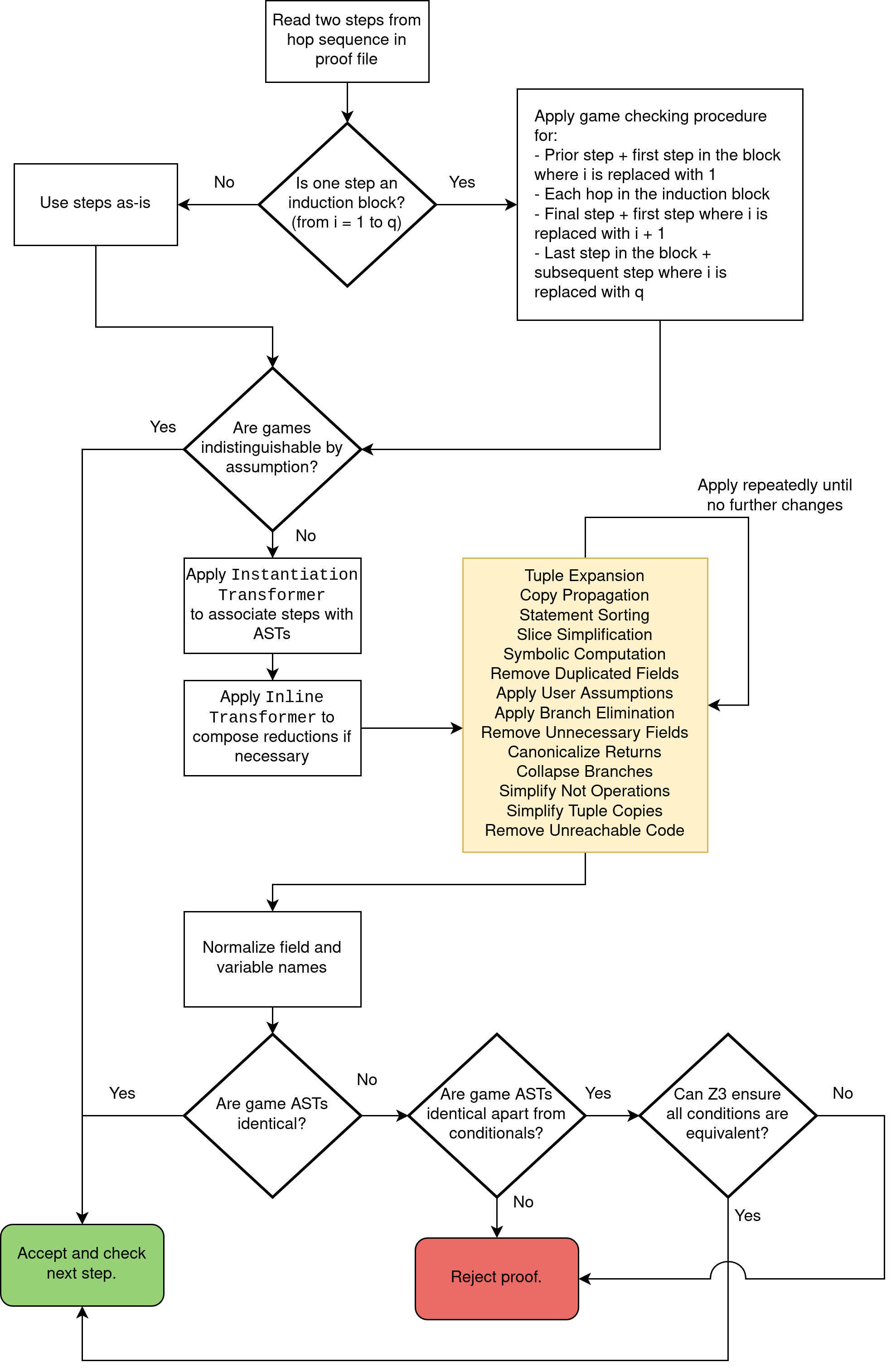
- The
InstantiationTransformertakes parameterized ASTs and rewrites parameters in terms of variables defined inside theletsection of the proof file. - The
InlineTransformeris used to inline function calls. This can happen during composition of games with reductions, or when calling a scheme method from within a game’s oracle. - “Tuple Expansion” takes tuples where the indices for all reads and writes can be statically determined, and rewrites them as multiple variable declarations.
- “Copy Propagation” removes variables that are copies of others
- “Statement Sorting” attempts to create a canonical ordering of statements within a block via a combination of depth first search and topological sorting. It also performs dead code elimination for statements that have no effect on the return value of an oracle.
- “Slice Simplification” is an advanced form of copy propagation used when one variable is a copy of another, but there is an intermediate concatenated bitstring that the variable is sliced out of
- “Symbolic Computation” takes integer variables and simplifies expressions they are used in into a simplest form via SymPy
- The “Remove Duplicated Fields” transformation searches each pair of fields in a game with the same type and unifies the values if it can be statically determined they share the same value throughout the game’s entire lifetime
- The “Apply User Assumptions” transformation utilizes assumptions about variables that a user can specify between pair of games to simplify conditions
- “Apply Branch Elimination” takes branches where the conditions are
trueorfalseand simplifies them - “Remove Unnecessary Fields” deletes any fields that do not effect the return value of any oracle
- “Canonicalize Returns” takes return statements that return variables and (when the value of the variable can be statically determined) rewrite them to return that variable
- “Collapse Branches” takes adjacent if/else-if branches with identical blocks of code and rewrites them into one branch where the condition is the OR of the previous two conditions
- “Simplify Not Operations” just takes
!(a == b)and rewrites it toa != b - “Simplify Tuple Copies” takes tuples of the form
[a[0], a[1], ..., a[n-1]]and rewrites them into justa - “Remove Unreachable Code” attempts to use Z3 to determine when a return statement is guaranteed to have executed, and deletes all code remaining in an oracle past that point
- Normalization of field and variable names just assigns each field a numeric name based on the first appearance in the AST.